Detect Damage By Images
Function Description: Performs deep learning-based detection on images and maps results back to 3D space for pavement damage detection, supporting both panoramic and planar cameras. Identifies six damage types (rutting, undulation, cracking, potholes, shallow pits, and bumps) to provide PCI calculation data. Compared to Detect Damage By Point Cloud, Detect Damage By Images achieves higher recognition accuracy and is recommended as the primary method when image data is available.
Steps
1.Click the Detect Damage By Images ![]() button to open the following dialog:
button to open the following dialog:
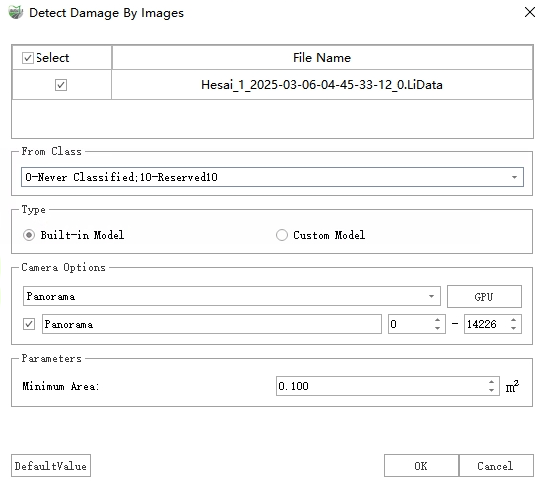
Detect Damage By Images Dialog
2.After configuring settings, click Detect to initiate damage detection.
3.Upon completion, two result types will be generated:
Vector Polygons: Results are stored as polygons in the "Damage Areas" layer, containing attributes for each damage instance including type, severity level, area, length, width, and maximum depth.
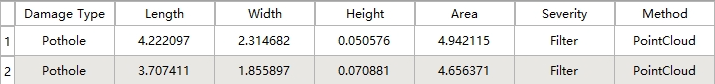
Damage Polygons
Point Cloud Attributes: Depth values are written to the "DamageDistance" attribute field and can be visualized:
Display: In the Display Mode window, select "Intensity" from the Color dropdown and enable With Pavement Damage:
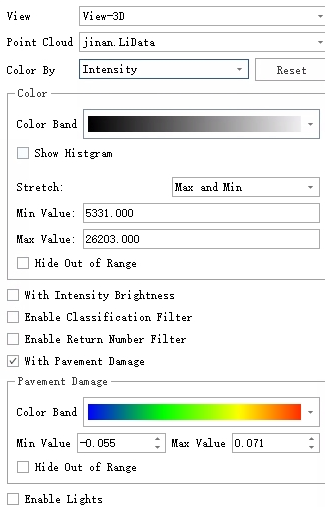
Pavement Damage Rendering Settings
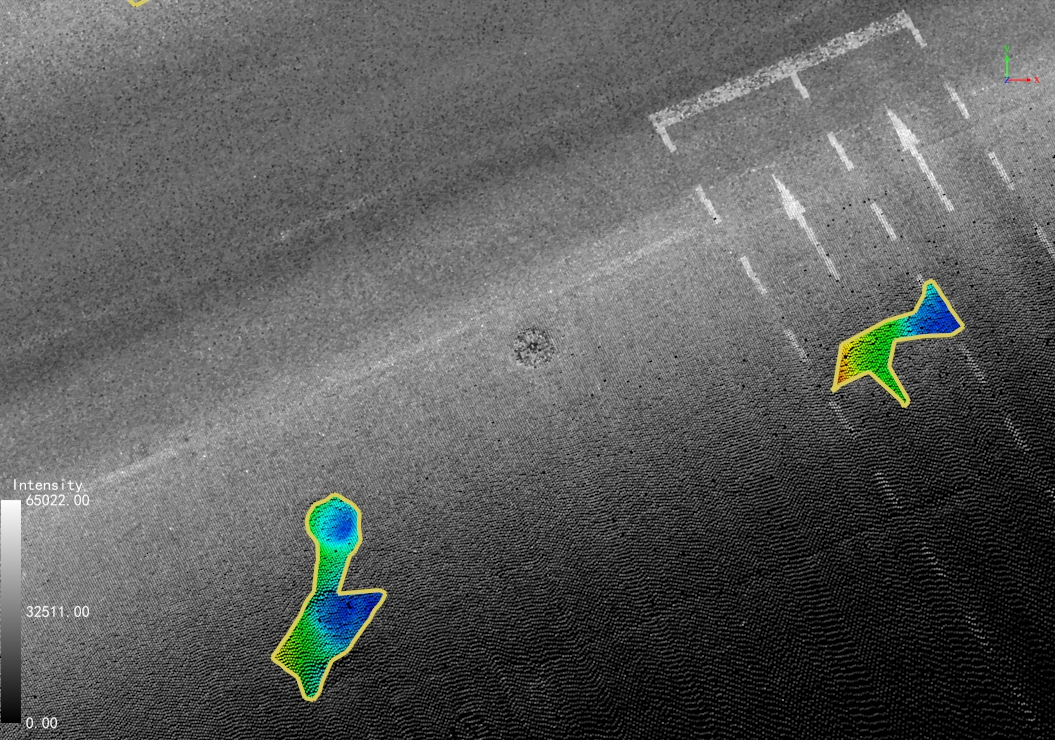

Pavement Damage Rendering
Depth Inspection: Use the Point Selection tool to examine individual "DamageDistance" values.
Parameter Settings
Point Cloud File: Select target point cloud data.
Source Class: Choose "Ground Points" if classification exists, otherwise select all classes. (Pre-classification recommended for optimal results)
Type: Two detection modes available:
Built-in Model: Uses integrated deep learning model for image analysis.
Custom Model: Processes pre-generated JSON results (filenames must match corresponding images). The system will reproject and merge these results into 3D space.
Camera Options: Specify camera type matching the model's training data (e.g., panoramic camera for panoramically-derived results).
Parameters:
Max Distance to Image: A distance threshold used to filter out damaged areas that are farther from the corresponding image than this value (damaged areas too far away tend to have larger re-projection errors).
Minimum Area: Filters damage regions smaller than specified value.