Viewshed Analysis
Function Overview
The Viewshed Analysis tool determines whether each pixel value in the terrain data is visible based on a series of viewpoint data.
Usage
Click on Terrain > Viewshed Analysis.
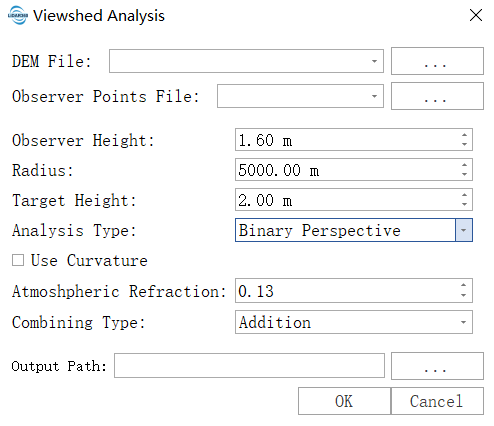
Parameter Settings
- Input DEM File: The input DEM file. For information on generating a DEM, see DEM Generation.
- Observer Points File: Input point-type vector file representing the positions of observation points.
- Observer Height: The height of the observer above the ground at their location. The default is 1.6 meters, approximately the height of a person’s eyes. For vehicle-mounted or rooftop devices, set it to the corresponding height.
- Radius: The radius for viewshed analysis. The default is set to 5000 meters, meaning the analysis is limited to within 5 kilometers around the observation point, and terrain beyond this range will be ignored. Reasonable setting can significantly shorten computation time.
- Target Height: The height of the target object being observed. The analysis result will judge whether the target at this height is visible. Set to 0 for analyzing ground visibility; set to 1.5–2 meters for analyzing pedestrians or vehicles; set to over 10 meters for analyzing buildings.
- Analysis Type: Determines the meaning of the output result:
- Binary Perspective: Generates a binary raster where pixel values of 0 indicate non-visible areas and 1 indicate visible areas. Suitable for basic visibility analysis.
- Depth Below the Horizon: Indicates how much higher a location must be to become visible.
- Horizon Boundary: Generates polar coordinate terrain profile data depicting the terrain contour around the observation point, suitable for skyline analysis and solar studies.
- Use Curvature: Whether to consider the Earth’s curvature. Must be checked for large-scale analyses (typically >10 km). The Earth is round, and over long distances, the curvature of the Earth can block the line of sight.
- Atmospheric Refraction: Also known as the vertical refraction coefficient, describes atmospheric refraction factors affecting visibility. The default value of 0.13 is standard, indicating that light bends slightly upward due to the atmosphere, making the actual visible distance slightly farther. Usually, keep the default value.
- Combining Type: When there are multiple observation points, how to merge the results:
- Addition: Uses arithmetic accumulation, with output pixel values being the sum of the visibility of each observation point. Suitable for coverage density analysis and blind spot identification.
- Minimum: Uses logical AND operation, marking a pixel as visible only if all observation points can see it. Suitable for critical area coordinated visibility assurance. (If any point is not visible, the pixel is 0; the minimum is 0, meaning visibility only if all points see it.)
- Maximum: Uses logical OR operation, marking a pixel as visible if any observation point can see it. Suitable for maximum visibility range analysis.
- Resampling: Processes resampling based on the raster pyramid structure. Different pyramid levels and resolutions are determined by specific data characteristics, with each successive layer downsampled at a 2:1 ratio.
- Resolution: The spatial resolution of the raster. For raster data with fewer than 1000 rows or columns, lower resolution levels will not be displayed. Higher resolution selections yield more precise results but may cause processing failures due to insufficient hardware resources.
- Resampling Method: The algorithm used for raster resampling.
- Output Path: Specifies the path for the output results.