ASL Trunk-based Tree Segmentation
Function Overview
This function first uses deep learning to extract the trunk, and then grows branches and leaves from the trunk as the seed point. Compared to Point Cloud Segmentation, it can handle point cloud data with trunk points obtained from devices with strong laser penetration, thus obtaining more accurate tree counts and locations.
Usage ##### Trunk-Based Individual Tree Segmentation
Functional Overview
This function first uses deep learning to extract tree trunks, then uses these trunks as seed points to grow branches and leaves. Compared to ALS Point Cloud Segmentation, it can process point cloud data containing trunk points acquired by equipment with strong laser penetration capability, thereby obtaining more accurate tree counts and positions.
Usage
Click Airborne Forestry > Trunk-Based Individual Tree Segmentation.
Parameter Settings
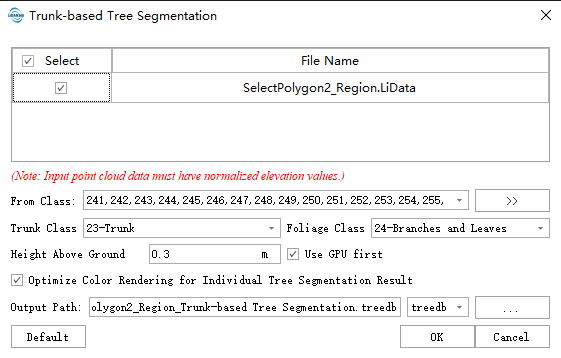
- Input Data: The input data must be normalized point cloud data. Please refer to Normalization or Normalization by Ground Class for normalization methods. The input file can be a single point cloud data file or a point cloud dataset; the data to be processed must be opened in the LiDAR360 software.
- Initial Class: The starting class of points participating in the segmentation. The default is all classes.
- Trunk Class (Default: "23"): The segmented trunks will be labeled with this class.
- Crown Class (Default: "23"): The segmented tree crowns will be labeled with this class.
- Prefer GPU: Whether to prioritize using the GPU for computation.
- Height Above Ground (meters) (Default: "0.3"): Only points above this height value participate in trunk extraction. This parameter is used to reduce the impact of ground point cloud thickness or undergrowth on the individual tree segmentation results. Setting this value too high can affect the accuracy of detecting tree DBH.
- Optimize Color Scheme for Segmentation Results (Selected by default): By reordering the ID information after individual tree segmentation, it can significantly resolve the issue of adjacent trees being assigned the same color.
- Output Path: After running, each point cloud data file will generate a corresponding segmentation result. The segmentation result is a comma-separated CSV file containing attributes such as Tree ID, x, y coordinate position, Tree Height, DBH, Crown Diameter, Crown Projection Area, and Crown Volume. Please refer to the Ground-Based LiDAR Individual Tree Segmentation Result File Format in the appendix. For methods to view the segmentation results, please refer to Viewing Point Cloud Segmentation Results.
- Default Values: Resets the parameter settings to their default values.
Impact of Parameters on Results:
| Parameter | Effect |
|---|---|
| Height Above Ground |  |
| Starting Segmentation Height |  |
@inproceedings{
author={López Serrano et al., 2022 F.R. López Serrano, E. Rubio, F.A. García Morote, M. Andrés Abellán, M.I. Picazo Córdoba, F. García Saucedo, E. Martínez García, J.M. Sánchez García, J. Serena Innerarity, L. Carrasco Lucas, O. García González, J.C. García González},
title={Artificial intelligence-based software (AID-FOREST) for tree detection: A new framework for fast and accurate forest inventorying using LiDAR point clouds},
booktitle={Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf., 113 (2022), Article 103014},
year={2022}
}
Click ALS ForestryForest > Trunk-based Tree Segmentation.

@inproceedings{
author={López Serrano et al., 2022 F.R. López Serrano, E. Rubio, F.A. García Morote, M. Andrés Abellán, M.I. Picazo Córdoba, F. García Saucedo, E. Martínez García, J.M. Sánchez García, J. Serena Innerarity, L. Carrasco Lucas, O. García González, J.C. García González},
title={Artificial intelligence-based software (AID-FOREST) for tree detection: A new framework for fast and accurate forest inventorying using LiDAR point clouds},
booktitle={Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf., 113 (2022), Article 103014},
year={2022}
}